Navigating Ethics in Academic Publishing Amidst the GenAI Revolution
Data scientist specializing in natural language processing and AI ethics.

Data scientist specializing in natural language processing and AI ethics.

Generative AI has become a transformative force in many fields. Academia is no different, experiencing a profound shift in how research and publishing are conducted.
Generative AI refers to advanced AI systems capable of creating new content, such as text, images, and even code. These systems, like OpenAI's ChatGPT, leverage large language models (LLMs) and natural language processing (NLP) to understand and generate human-like responses.

Academic publishing has evolved significantly from its traditional roots. The digital age brought about online journals and open access, but generative AI represents a more radical change.
It challenges the very core of authorship and originality. The ability to generate human-like text, as described in the article "GenAI et al.: Cocreation, Authorship, Ownership, Academic Ethics and Integrity in a Time of Generative AI", is reshaping the academic landscape.
The integration of generative AI into academic processes raises serious ethical questions. Academic integrity, built on honesty, trust, and accountability, faces new challenges.
There are instances where AI has been misused, leading to academic misconduct. Students and researchers might use AI to generate entire papers, blurring the lines between original work and AI-generated content.
AI can be a double-edged sword. It can assist in research but also facilitate plagiarism, as highlighted in the Wiley report, "The Latest Insights into Academic Integrity".
The question of authorship becomes complex when AI is involved. Determining the extent of human versus AI contribution is crucial for maintaining ethical standards.
Copyright laws traditionally require human authorship. AI-generated content challenges these laws, creating a gray area regarding ownership and intellectual property rights.

Existing ethical frameworks often fall short in addressing the unique challenges posed by generative AI. They were designed for a pre-AI era and need significant updates.
Transparency is key. Researchers should disclose when and how AI is used in their work, ensuring accountability.
Documenting AI contributions helps clarify roles and responsibilities. It establishes a clear record of human and AI involvement in the research process.
For example, the APA and MLA style guides now include recommendations for citing LLM-generated materials. This information can be found in the article "AI & Academic Integrity".
Generative AI offers numerous opportunities to enhance research efficiency. It can assist in literature reviews, data analysis, and even drafting sections of papers, freeing up researchers to focus on more complex tasks.
For instance, AI can help in generating ideas and understanding difficult content. This benefit is further elaborated on in the article "How Generative AI is Shaping the Future of Work".
New models of collaboration between humans and AI are emerging. These models leverage the strengths of both, creating a synergistic relationship that can lead to innovative research outcomes.
Researchers can use AI to analyze large datasets, identifying patterns that might be missed by human analysis. This collaboration can lead to groundbreaking discoveries, as seen in fields like healthcare, discussed in "Navigating the Tightrope: Merging Innovation and Ethics in AI Healthcare".
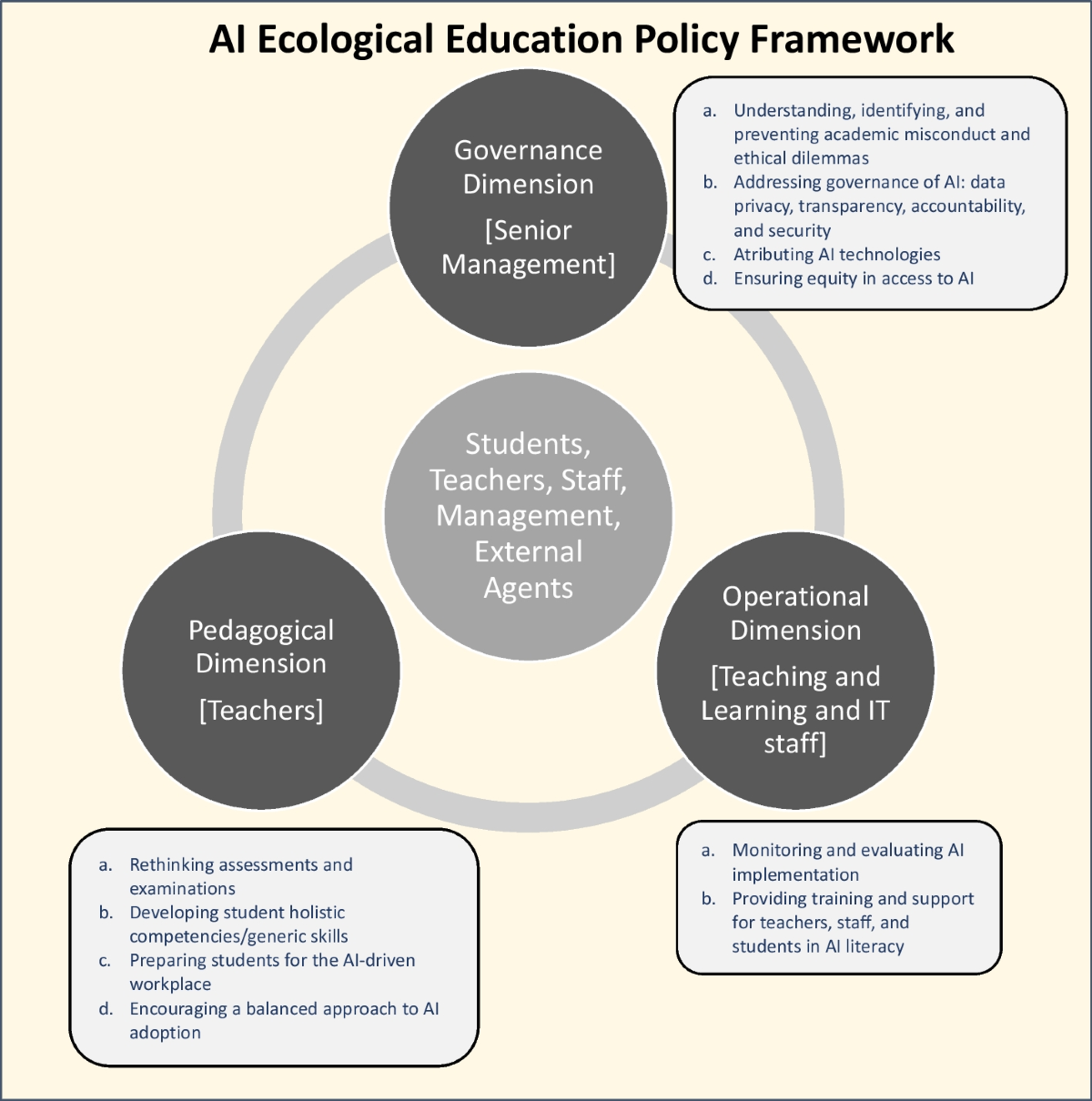
The academic community must engage in ongoing dialogue to adapt standards and practices. This includes revisiting the definition of authorship and developing new guidelines for AI use.
Comprehensive policies are needed to address the ethical challenges posed by AI. These policies should promote responsible AI use while preserving academic integrity.
Institutions must establish clear guidelines and provide training for researchers and students. For example, RTI's framework for responsible AI use, detailed in "Responsible Use of Artificial Intelligence in Research", offers a model for other organizations to follow.
Key Takeaways:
— in AI in Business
— in AI in Business
— in Healthcare AI
— in GenAI
— in Sustainability and AI